What Is an HMO Plan?
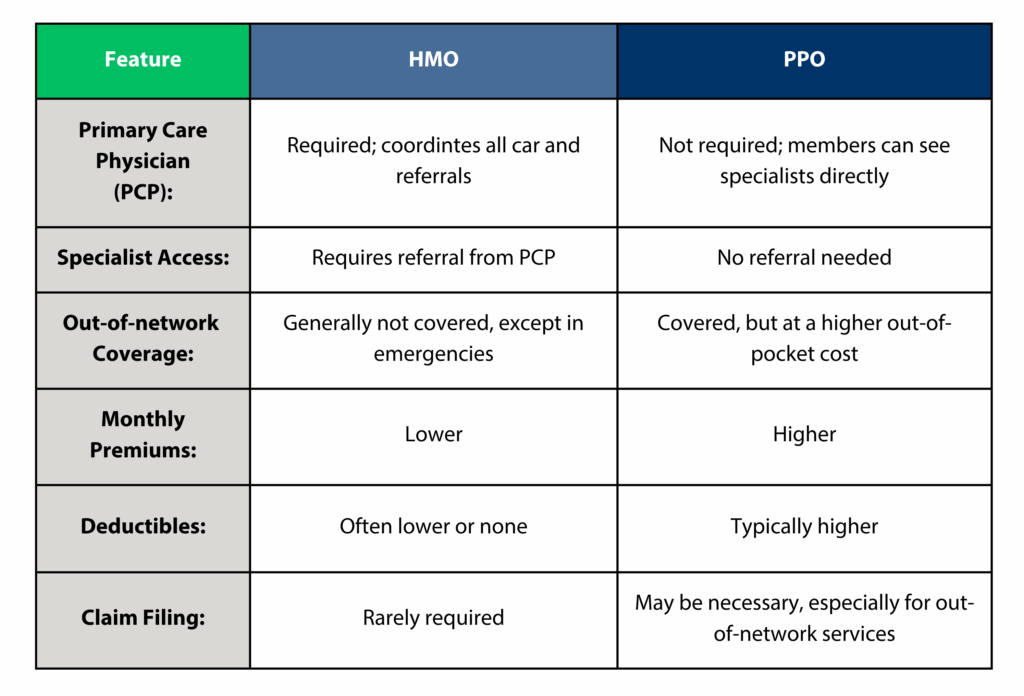
An HMO, or Health Maintenance Organization, is a type of health insurance plan that requires members to choose a primary care physician (PCP) who coordinates all healthcare services. Referrals from the PCP are necessary to see specialists. Coverage is typically limited to in-network providers, except in emergencies.
Key Features of HMOs
Network Restrictions: Services are limited to in-network providers, except for emergencies.
Primary Care Physician (PCP): Members must select a PCP who manages their care and provides referrals to specialists.
Cost Structure: Generally, HMOs have lower monthly premiums and out-of-pocket costs, often with minimal or no deductibles.
Claim Process: Since services are within the network, members usually don’t need to file claims; providers bill the HMO directly.
What Is a PPO Plan?
A PPO, or Preferred Provider Organization, offers more flexibility in choosing healthcare providers. Members can see any healthcare provider without a referral, including out-of-network providers, though at a higher cost.
Key Features of PPOs
Network Flexibility: Members can see both in-network and out-of-network providers without referrals.
Primary Care Physician (PCP): Not required; members can see specialists directly.
Cost Structure: PPOs typically have higher monthly premiums and deductibles compared to HMOs but provide broader access to various healthcare providers.
Claim Process: Members may need to file claims, especially when using out-of-network services.
Choosing Between HMO and PPO
Opt for an HMO if:
You prefer lower premiums and out-of-pocket costs.
You’re comfortable with a PCP managing your care and providing referrals.
You don’t anticipate needing out-of-network services.
Opt for a PPO if:
You desire greater flexibility in choosing healthcare providers.
You want the option to see specialists without referrals.
You’re willing to pay higher premiums for broader access.
Medicare Advantage: HMO vs. PPO
Medicare Advantage plans, also known as Medicare Part C, are offered by private insurance companies and combine Medicare Parts A and B coverage. These plans can be structured as either HMOs or PPOs.
Medicare HMO Plans
Network Restrictions: Require members to use in-network providers, except in emergencies.
Primary Care Physician (PCP): Required; coordinates all care and referrals.
Cost Structure: Typically have lower premiums and out-of-pocket costs.
Medicare PPO Plans
Network Flexibility: Allow members to see both in-network and out-of-network providers without referrals.
Primary Care Physician (PCP): Not required.
Cost Structure: Generally have higher premiums and out-of-pocket costs but offer greater flexibility.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between HMO and PPO plans is essential for selecting the health insurance that best fits your needs and budget. Consider factors like provider flexibility, cost, and whether you prefer coordinated care through a PCP when making your decision.
Still unsure which plan is right for you?
Click the button below to schedule a free consultation with one of our licensed Medicare experts. We’ll help you make a confident, informed choice that supports your health and peace of mind.
